The effect of running speed on knee mechanical loading in females during side cutting
Abstract
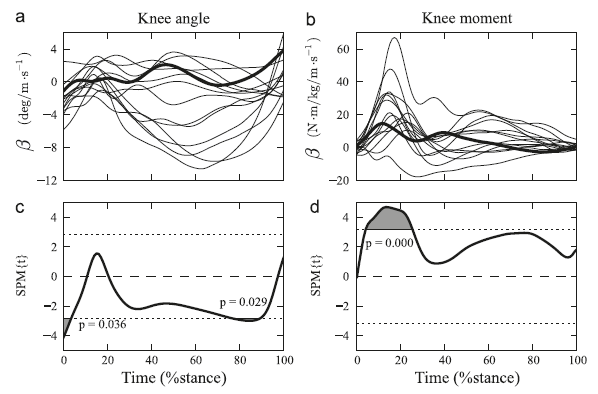
Background: Side cutting involves mechanical loading of the knee which has been associated with anterior cruciate ligament injury risk. Despite a fast growing body of research, the relationship between loading mechanisms and running speed is still unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate how running speed determines a likely trade-off between task achievement and actual mechanical loading. Methods: Fourteen female participants (mean age¼ 20.6 70.7 yr, height ¼ 1.66 7 0.05 m, mass ¼ 57.5 7 6.9 kg) performed 451 side cutting manoeuvres at 2, 3, 4 and 5 m sÀ1 approach speeds. Three dimensional motion and ground reaction forces were recorded to calculate whole body centre of mass (CoM) velocity and lower limb kinematics and kinetics, focusing on knee flexion angle at touch-down and peak knee valgus loading during weight acceptance. One-way repeated measures ANOVA and one-dimensional statistical parametric mapping were used to identify significant speed effects on task achievement and mechanical loading. Results: Analysis of CoM velocities revealed that side cutting manoeuvres at higher running speeds matched the task requirements to a lesser extent. Despite a gradual increase of anterior–posterior deceleration and medio-lateral acceleration with running speed, knee loading mechanisms only reached meaningful levels from a 4 m/s running speed. Conclusion: Our results confirmed a trade-off between task achievement and actual mechanical loading. This identified a need for standardisation of reporting running speeds. Taking into account also safety considerations, standardisation of a 4 m sÀ1 running speed is proposed for female athletes. & 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.