Vector field statistics for objective center-of-pressure trajectory analysis during gait, with evidence of scalar sensitivity to small coordinate system rotations
Abstract
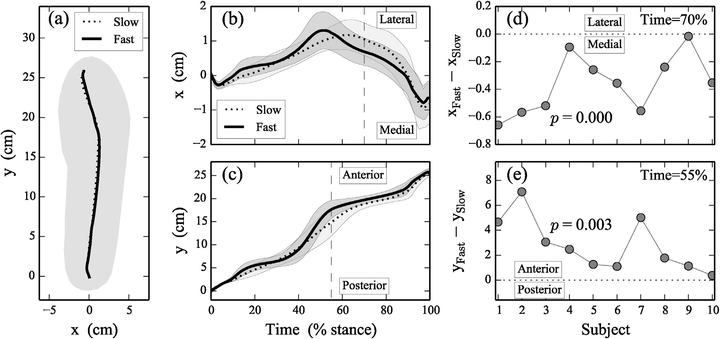
Center of pressure (COP) trajectories summarize the complex mechanical interaction between the foot and a contacted surface. Each trajectory itself is also complex, comprising hundreds of instantaneous vectors over the duration of stance phase. To simplify statistical analysis often a small number of scalars are extracted from each COP trajectory. The purpose of this paper was to demonstrate how a more objective approach to COP analysis can avoid particular sensitivities of scalar extraction analysis. A previously published dataset describing the effects of walking speed on plantar pressure (PP) distributions was re-analyzed. After spatially and temporally normalizing the data, speed effects were assessed using a vector-field paired Hotelling’s T2 test. Results showed that, as walking speed increased, the COP moved increasingly posterior at heel contact, and increasingly laterally and anteriorly between $60 and 85% stance, in agreement with previous independent studies. Nevertheless, two extracted scalars disagreed with these results. Furthermore, sensitivity analysis found that a relatively small coordinate system rotation of 5.58 reversed the mediolateral null hypothesis rejection decision. Considering that the foot may adopt arbitrary postures in the horizontal plane, these sensitivity results suggest that non-negligible uncertainty may exist in mediolateral COP effects. As compared with COP scalar extraction, two key advantages of the vector-field approach are: (i) coordinate system independence, (ii) continuous statistical data reflecting the temporal extents of COP trajectory changes. ß 2014 Elsevier B.V. This is an open access article under the CC BY license (http://creativecommons.org/ licenses/by/3.0/).