A force profile analysis comparison between functional data analysis, statistical parametric mapping and statistical non-parametric mapping in on-water single sculling
Abstract
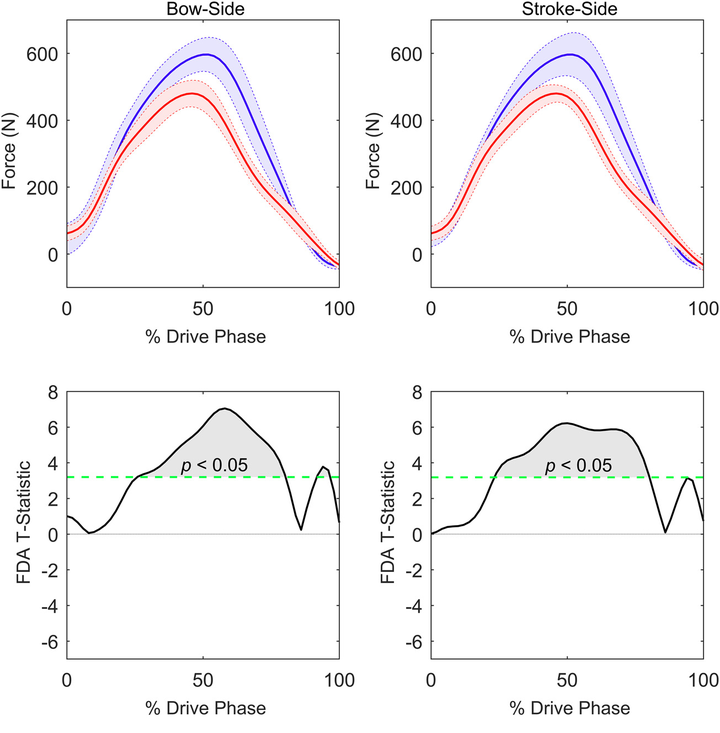
Objectives: To examine whether the Functional Data Analysis (FDA), Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM) and Statistical non-Parametric Mapping (SnPM) hypothesis testing techniques differ in their ability to draw inferences in the context of a single, simple experimental design. Design: The sample data used is cross-sectional (two-sample gender comparison) and evaluation of differences between statistical techniques used a combination of descriptive and qualitative assessments. Methods: FDA, SPM and SnPM t-tests were applied to sample data of twenty highly skilled male and female rowers, rowing at 32 strokes per minute in a single scull boat. Statistical differences for gender were assessed by applying two t-tests (one for each side of the boat). Results: The t-statistic values were identical for all three methods (with the FDA t-statistic presented as an absolute measure). The critical t-statistics (tcrit ) were very similar between the techniques, with SPM tcrit providing a marginally higher tcrit than the FDA and SnPM tcrit values (which were identical). All techniques were successful in identifying consistent sections of the force waveform, where male and female rowers were shown to differ significantly (p textless 0.05). Conclusions: This is the first study to show that FDA, SPM and SnPM t-tests provide consistent results when applied to sports biomechanics data. Though the results were similar, selection of one technique over another by applied researchers and practitioners should be based on the underlying parametric assumption of SPM, as well as contextual factors related to the type of waveform data to be analysed and the experimental research question of interest.